The debate between private vs public health insurance is a nuanced one, with each system presenting its own set of advantages and disadvantages. As individuals navigate the intricacies of healthcare coverage, understanding the fundamental distinctions between these two models is paramount.
Contents
Public Health Insurance: The Pillar of Universal Coverage
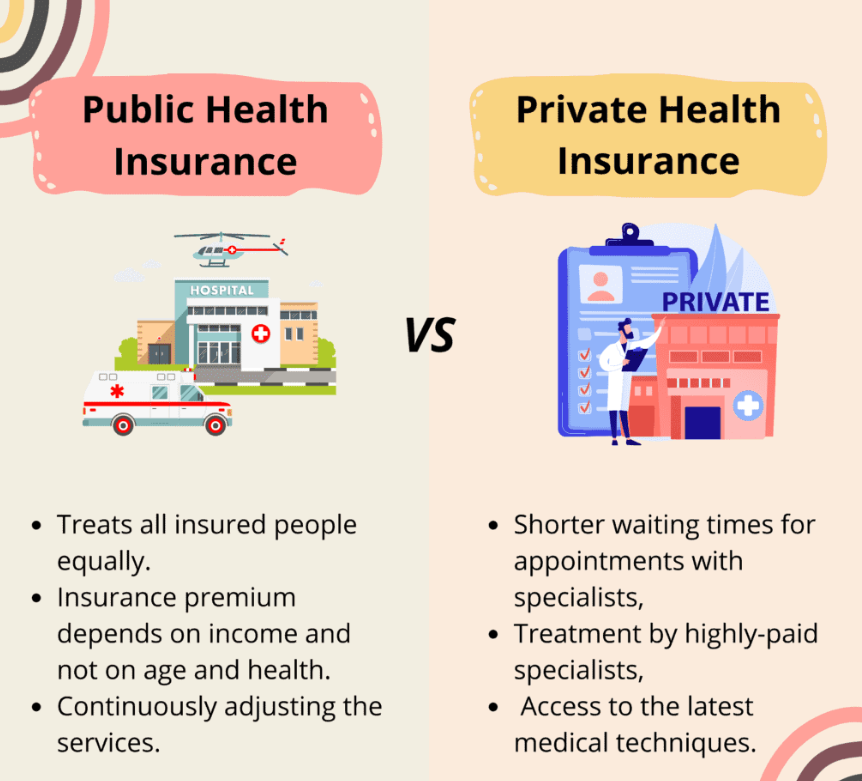
Public health insurance, often funded through taxation or mandatory contributions, aims to provide affordable healthcare access to all citizens, regardless of their income or health status. This system fosters a sense of shared responsibility, ensuring that even the most vulnerable populations have a safety net in times of medical need.
Advantages of Public Health Insurance
- Universality: Public health insurance systems prioritize inclusivity, extending coverage to every individual within a nation. This approach minimizes disparities in healthcare access, promoting a more equitable society.
- Affordability: By pooling resources and spreading risk across a large population, public health insurance systems can negotiate lower healthcare costs, making coverage more affordable for all.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: Public health insurance systems tend to streamline administrative processes, minimizing the complexity and paperwork associated with healthcare coverage.
Challenges of Public Health Insurance

- Waiting Times: In some instances, public health insurance systems may face challenges with long waiting times for non-emergency procedures due to high demand and resource constraints.
- Limited Provider Choice: Depending on the system design, individuals may have limited flexibility in choosing their healthcare providers, potentially impacting their preferred care options.
- Potential for Overutilization: The universal nature of public health insurance systems may lead to increased utilization of healthcare services, potentially straining resources and contributing to rising costs.
Private Health Insurance: The Realm of Choice and Flexibility
Private health insurance, typically purchased by individuals or employers, offers a range of coverage options tailored to individual needs and preferences. This model emphasizes personal responsibility and choice, allowing individuals to select plans that best suit their financial capabilities and healthcare requirements.
Advantages of Private Health Insurance
- Greater Provider Choice: Private health insurance systems often provide individuals with a wider selection of healthcare providers, empowering them to choose specialists and facilities that align with their preferences.
- Shorter Waiting Times: Private health insurance can often facilitate faster access to non-emergency procedures, minimizing delays and ensuring timely care.
- Tailored Coverage Options: Private health insurance plans can be customized to address specific healthcare needs, allowing individuals to select coverage levels and benefits that match their priorities.
Challenges of Private Health Insurance
- Cost: Premiums for private health insurance can be substantial, potentially creating a financial burden for individuals and families, particularly those with pre-existing conditions or limited incomes.
- Coverage Gaps: Even with private health insurance, certain services or treatments may not be fully covered, leading to unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
- Complex Administrative Processes: Private health insurance systems may involve complex administrative processes, requiring individuals to navigate intricate paperwork and billing procedures.
The Hybrid Model: Striking a Balance
In many countries, a hybrid model combining elements of both public and private health insurance has emerged. This approach aims to leverage the strengths of each system while mitigating their limitations.
Benefits of a Hybrid Model
- Increased Accessibility: A hybrid model can expand healthcare access by providing a public safety net while offering individuals the option to purchase additional private coverage for enhanced benefits and services.
- Reduced Financial Burden: By integrating public and private financing mechanisms, a hybrid model can alleviate the financial burden on individuals while ensuring a sustainable healthcare system.
- Enhanced Provider Choice: A hybrid model can foster a competitive environment among healthcare providers, potentially leading to improved quality and greater patient satisfaction.
Challenges of a Hybrid Model
- Complexity: Designing and implementing a successful hybrid model requires careful coordination and collaboration between public and private stakeholders, which can be challenging to achieve.
- Potential for Inequality: A hybrid model may inadvertently create disparities in healthcare access if private coverage becomes too expensive or inaccessible for certain populations.
- Regulatory Challenges: Striking a balance between public oversight and market forces in a hybrid model requires effective regulation and monitoring to ensure fairness and prevent abuses.
Factors Influencing the Choice
Several factors influence the choice between private vs public health insurance, including:
- Individual Needs and Preferences: Individuals with specific healthcare needs or preferences may opt for private insurance to access specialized care or a broader range of providers.
- Financial Resources: Private health insurance premiums can be costly, making public insurance a more viable option for individuals with limited financial means.
- Country-Specific Context: The availability and quality of public and private health insurance options vary significantly across countries, influencing individual choices.
Conclusion
The debate between private vs public health insurance is complex and multifaceted, with no one-size-fits-all answer. Each system presents its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal choice ultimately depends on a range of factors.
Read More: Life Insurance for Those with Pre-Existing Conditions: An Exclusive Guide