In our increasingly interconnected world, making international phone calls has become commonplace. Whether it’s to connect with family abroad, conduct global business, or simply stay in touch with friends on an overseas adventure, understanding how international dialing works is essential. For many Americans, the process of dialing internationally often involves a string of numbers that can seem confusing. This article aims to demystify international calling, with a particular focus on the elusive 006 country code and what it means for callers in the United States.
Contents
The Anatomy of an International Call from the U.S.
Before we delve into specific country codes, it’s helpful to understand the general structure of an international call originating from the United States. To place a call to almost any country outside of the North American Numbering Plan (which includes the U.S., Canada, and many Caribbean nations), you’ll typically follow this sequence:
- International Access Code (Exit Code): For calls from the U.S., this is almost always “011”. This code signals to your phone carrier that you’re about to make an international call.
- Country Code: This is a one- to three-digit code assigned to a specific country or territory by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). This code directs your call to the correct country.
- Area Code (or City Code): Many countries have internal area codes that narrow down the geographical region within that country.
- Local Phone Number: Finally, the individual phone number of the person or business you’re trying to reach.
So, the general format looks like: 011 + Country Code + Area Code (if applicable) + Local Phone Number.
The Mystery of the 006 Country Code
You might be searching for the 006 country code, expecting to find a direct match to a single country. However, the international numbering plan, as defined by the ITU, doesn’t actually assign a primary country code of 006. Country codes typically begin with a single digit that broadly categorizes a region of the world. For instance:
- Zone 1: North America (e.g., +1 for the U.S. and Canada)
- Zone 2: Africa
- Zones 3 & 4: Europe
- Zone 5: South and Central America
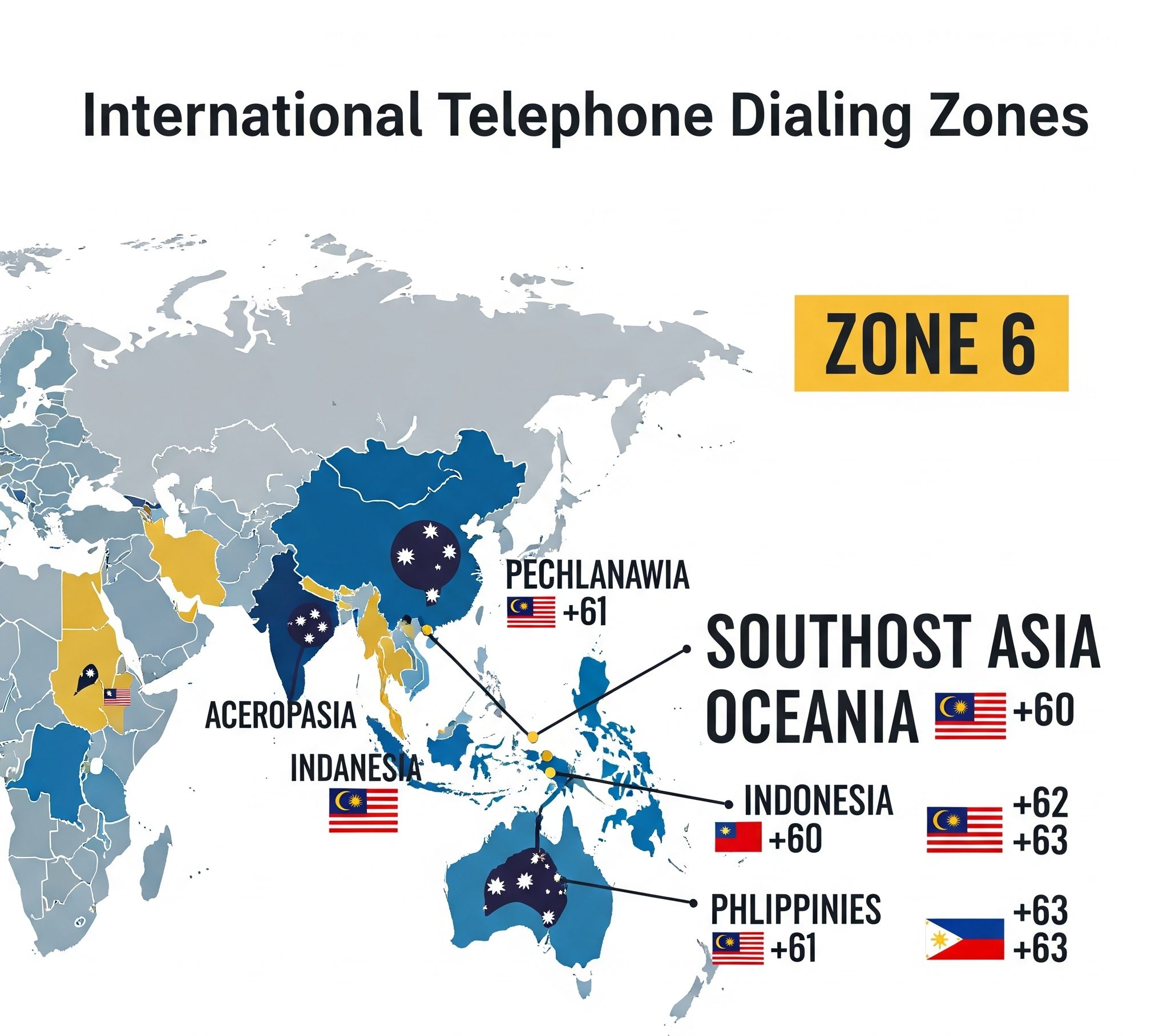
- Zone 6: Southeast Asia and Oceania
- Zone 7: Russia and Kazakhstan
- Zone 8: East Asia and Special Services
- Zone 9: West, Central, and South Asia, and parts of Southern Europe
The “00” prefix you often see before a country code, like “00” followed by a specific country code, usually represents an international access or exit code, depending on the country you’re calling from. For example, many countries use “00” as their international access code, similar to the “011” used in the U.S.
So, if you’ve encountered what appears to be a “006 country code,” it’s highly probable that the “00” part is the international access code from a specific foreign country, and the “6” is actually the first digit of a country code within Zone 6 (Southeast Asia and Oceania).
For example:
- +60 is the country code for Malaysia.
- +61 is the country code for Australia.
- +62 is the country code for Indonesia.
- +63 is the country code for the Philippines.
- +64 is the country code for New Zealand.
- +65 is the country code for Singapore.
- +66 is the country code for Thailand.
Therefore, if someone from, say, a country that uses “00” as its international access code were to dial Malaysia, they would dial 0060 followed by the rest of the Malaysian number. To an American caller, this might mistakenly look like “006 country code.”
Navigating International Dialing from the U.S.
To avoid confusion and ensure your international calls connect successfully, always remember to use the U.S. international access code “011” followed by the actual country code.
Here’s a quick guide for some popular destinations in the Zone 6 region:
- To call Australia: Dial 011 + 61 + area code + local number.
- To call New Zealand: Dial 011 + 64 + area code + local number.
- To call Singapore: Dial 011 + 65 + local number.
- To call Thailand: Dial 011 + 66 + local number.
- To call Malaysia: Dial 011 + 60 + area code + local number.
Always double-check the specific country code and any necessary area codes for your desired destination. Reliable resources like online international dialing guides or your phone service provider’s website can provide the most up-to-date and accurate information.
The Evolution of Global Communication
The system of international dialing codes, standardized by the ITU in the mid-20th century, was a monumental step in making global communication accessible. Before these codes, international calls often required operators and could be a cumbersome, time-consuming, and expensive endeavor. The systematic assignment of codes allowed for direct dialing across borders, facilitating personal connections and global commerce.
conclusion
While the concept of a “006 country code” as a standalone entity is a misinterpretation of how international dialing functions, it highlights the nuances of global telecommunications. For American callers, understanding the “011” exit code and then identifying the correct country code for your destination is key to connecting with the world beyond U.S. borders. As technology continues to evolve, simplifying communication even further, the fundamental principles of international dialing remain an important piece of our global infrastructure.







